Things for Unit 8 you should UNDERSTAND, KNOW, and be able to DO...
Understand:
- The evidence that is used to discover Earth's History.
- That geologic history can be reconstructed by determining the age of rocks, sequence of rock layers, and studying fossils.
Know:
- Relative Dating - The Principles of Stratigraphy
- Age relationships among bodies of rocks can be determined using principles of original horizontality, superposition, inclusions, cross-cutting relationships, contact metamorphism, and unconformities.
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Fossils are the remains and traces of past life, which have led to understanding the pattern of evolution of life and the planet.
- Fossils and rocks can be used to infer past environmental conditions.
- The evolution of Earth’s atmosphere and oceans is recorded in the fossil and rock record.
- The correlation of index fossils and rocks worldwide has led to the creation of the Geologic Time Scale.
- Geologic history is divided into time units based on the fossil and rock record.
- Human existence is very brief compared to the expanse of geologic time.
- Index fossils are widespread; they are the remains of organisms that existed within a short geologic time period.
- Absolute Dating
- The absolute age of fossils and rocks can be determined using the decay rate of radioactive isotopes.
- The regular rate of nuclear decay of radioactive isotopes allows geologists to determine the absolute age of materials found in fossils and rocks.
- Half-life is the amount of time it takes for half of a radioisotope to decay.
- Because of its relatively short half-life and its presence in living tissue, C-14 is used to find the absolute age of more recent organic materials.
Vocab Terms: stratigraphy, law of superposition, extrusion/intrusion, folds/faults, cross-cutting, original horizontality, contact metamorphism, unconformity, index fossil, relative age, correlation, evolution, geologic time, absolute age/radioactive dating, radioactive decay, isotope, half-life, parent material, daughter/decay product
Extended Vocabulary: uniformitarianism, outgassing, mass extinction, names of fossils, geologic time divisions
Do:
- Determine relative age of rock layers using Principles of Stratigraphy.
- Correlate rock layers using Principles of Stratigraphy & index fossils.
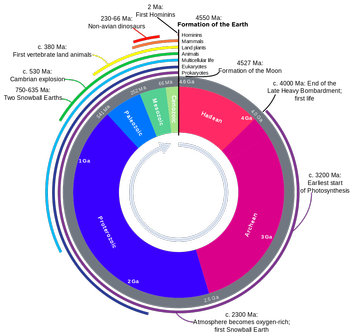
- Interpret the Geologic Time Chart (ESRT pg. 8-9).
- Identify Geologic Time divisions on ESRT pg. 8-9.
- Correlate information on ESRT pg. 8-9 to Generalized Bedrock Geology of NYS, ESRT pg. 3.
- Calculate absolute age using radioactive decay and half-life (ESRT pg. 1).